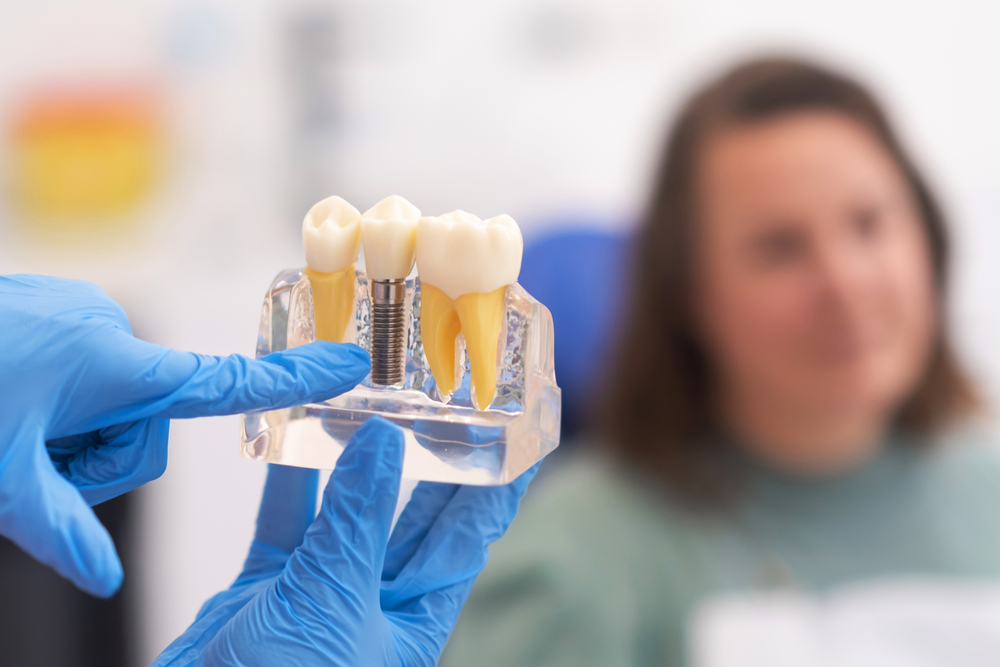
Dental implants have become a highly sought-after solution for tooth replacement in Australia, offering a long-term, natural-looking alternative to dentures and bridges. As this advanced treatment grows in popularity, so too does the importance of strict regulatory standards to ensure patient safety and treatment efficacy. In Australia, the framework governing dental implants is comprehensive, involving multiple authorities and professional guidelines. This article explores the key dental regulations, standards, and requirements in place to maintain the high quality and safety of dental implant procedures across the country.
Overview of Dental Implants in Australia
Dental implants are titanium or ceramic posts surgically placed into the jawbone to support artificial teeth. They are commonly used to replace missing teeth, restore oral function, and improve aesthetics. In Australia, their use has expanded significantly due to advancements in technology and growing public awareness.
However, because the procedure is surgical and involves both restorative and prosthetic dentistry, dental implants are subject to rigorous regulations by professional and government bodies. These ensure that practitioners are properly trained, materials are safe, and patients are adequately informed and protected.
Regulatory Bodies Involved
In Australia, the key regulatory and professional bodies overseeing the use of dental implants include:
- The Dental Board of Australia (DBA)
- The Australian Health Practitioner Regulation Agency (AHPRA)
- The Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA)
- The Australian Dental Association (ADA)
Each of these organizations plays a vital role in maintaining standards across the dental industry.
The Dental Board of Australia (DBA)
The DBA regulates dental practitioners under the National Registration and Accreditation Scheme. It sets mandatory guidelines on scope of practice, continuing professional development (CPD), infection control, and advertising. Dentists placing dental implants must comply with all DBA requirements, including maintaining professional competency through accredited implant training and CPD programs.
The DBA also enforces the Code of Conduct for Registered Health Practitioners, which covers ethical practices, patient consent, record-keeping, and more—essential elements in any implant treatment plan.
The Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA)
The TGA is responsible for regulating medical devices in Australia, including dental implants and associated components like abutments and surgical instruments. Only TGA-approved implants can be legally used by dental professionals. These devices must meet stringent safety and performance criteria, ensuring biocompatibility, durability, and clinical effectiveness.
Practices using non-approved or imported implants not listed on the Australian Register of Therapeutic Goods (ARTG) risk serious legal and ethical consequences.
The Australian Dental Association (ADA)
The ADA provides best-practice clinical guidelines and policies relating to dental implants. While not a regulatory authority, its publications are widely respected and often form the basis for treatment protocols across clinics. The ADA also supports practitioner education and public awareness regarding implant options, risks, and post-operative care.
Qualifications and Scope of Practice
Not all dentists are qualified to place dental implants. In Australia, general dentists can perform implant procedures only if they have undertaken formal implant training and can demonstrate proficiency. More complex cases are typically referred to specialists such as oral and maxillofacial surgeons, prosthodontists, or periodontists.
Under the DBA’s Scope of Practice Registration Standard, all procedures must be performed within the individual’s scope of education, training, and competence. Dentists are legally and ethically obligated not to perform implant surgery unless they are properly qualified and insured to do so.
Informed Consent and Patient Rights
An essential regulatory requirement for any dental procedure, especially surgical ones like dental implants, is obtaining informed consent. Dentists must provide patients with clear, detailed information about:
- The nature of the procedure
- Risks and benefits
- Alternatives (such as dentures or bridges)
- Expected costs and outcomes
- Post-treatment care and follow-up
Patients should be given the opportunity to ask questions and make decisions free of pressure. The failure to obtain proper consent can lead to legal action and disciplinary consequences from the DBA.
Infection Control Standards
Infection control is another critical area governed by regulation. Dental clinics must adhere to the Australian Guidelines for the Prevention and Control of Infection in Healthcare, as well as DBA’s Infection Prevention and Control Guidelines.
Because dental implants involve surgical intervention, strict sterilisation procedures, use of personal protective equipment (PPE), and surface decontamination protocols must be followed. These measures protect both patients and clinicians from the transmission of infectious diseases.
Advertising and Marketing Regulations
Practices offering dental implants must also follow strict advertising regulations set out by AHPRA and the DBA. Misleading claims, promises of guaranteed success, or testimonials that create unreasonable patient expectations are prohibited.
Any marketing materials or website content discussing dental implants must present factual, balanced, and substantiated information. Failure to comply can result in penalties, public reprimand, or even deregistration.
As demand for dental implants continues to grow in Australia, maintaining robust regulatory oversight is essential. The combined efforts of the Dental Board of Australia, TGA, AHPRA, and ADA ensure that practitioners are qualified, materials are safe, and patients are well-informed and protected.
Whether you’re a patient considering dental implants or a clinician offering them, understanding the regulations and standards governing implant dentistry is crucial for successful, ethical outcomes. Australia’s comprehensive regulatory framework ensures that dental implants remain a safe and effective solution for restoring smiles nationwide.